
(Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
One valuable technology in assisting people do to work was the invention of gears. Gears consist of a system of cogs that takes energy from an input source, such as flowing water, and convert it to an output source, such as a pump. The oldest archeological evidence for gears dates to about 230 BCE in China, however evidence of geared technology prior to that time is referenced from ancient Imperial Chinese manuscripts.
A Brief History of the Invention of Gears

(Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
The invention of gears are a natural extension from the invention of the wheel. They appear to have been invented in China but it was the Greeks who demonstrated their widespread use. Archimedes is believed to have used gears in his constructions and in the 4th century BCE Aristotle provided one of the earliest descriptions of gear-like devices. By 100 BCE they were being used across much of Greek civilization.
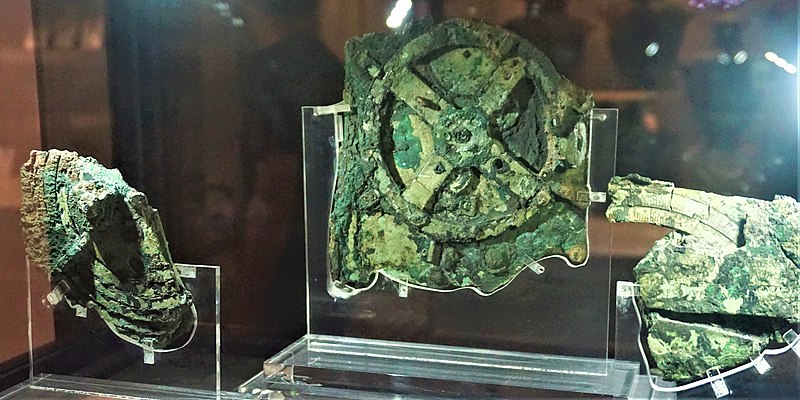
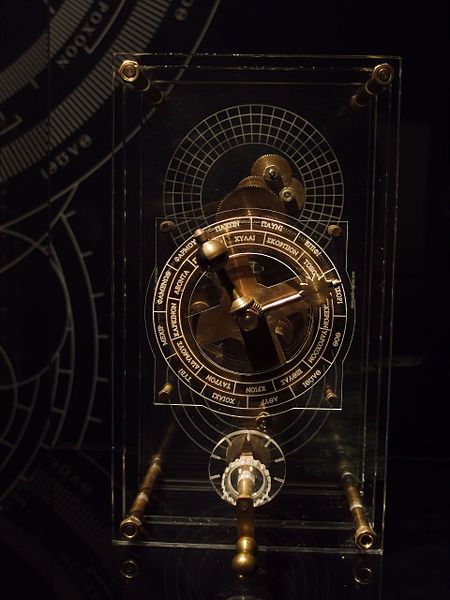
The discovery of the Antikythera mechanism, dubbed the worlds first analogue computer, is one of the earliest examples of a complex mechanism using a combination of gears. This device was discovered in 1901 from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera. The instrument was used to predict astronomical positions. It is a complex, hand-wound device consisting of 30 bronze gears. Like a clock, it had a circular face with several hands that displaced times of celestial objects such as the Sun, Moon, and known planets. Winding the device forward or backward would move the hands at various speeds thought the interconnecting gear train. Not all of the pieces have been fully recovered so the precise mechanisms and exact purpose of the device is not fully understood, but it does unequivocally show that gears were being used in complex devices by 100 BCE.
A Remarkable Level of Flexibility Leads to a Remarkable Level of Functionality
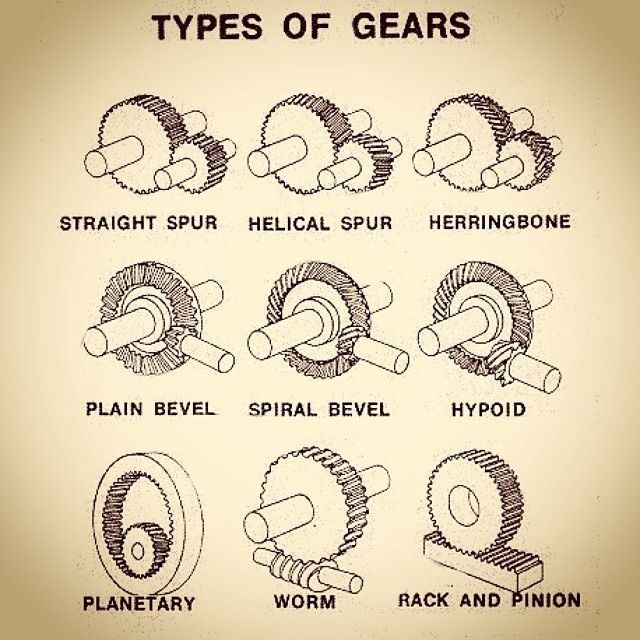
There are many ways to design and combine gears making them extremely versatile. The various different types of gears can be broadly classified by the orientation of their axes. There are other characteristic differences such as gear tooth design and gear shape.
The first category is parallel axes. Spur gears and helical gears have parallel axes. This design is easy to manufacture and produces efficient power and motion transmission. The next category is intersecting axes. Gears such as plain bevel and spiral bevel have intersecting axes. These also have high transmission efficiencies. A final category that is non-parallel and non-intersecting such as worm gears. These typically have lower motion and power efficiencies than the prior two categories. Each type provides a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Some operate more smoothly and quietly while others provide strength and durability where needed. Ease of manufacturing, which is related to costs, also varies across the different types of gears.
Putting Gears to Use
The earliest gears had a few broad applications. They were used in large machinery such as water mills and irrigation systems where they were needed to transmit considerable power. Water mills were increasingly used from the time of the Romans all the way through the Middle Ages of Europe. A secondary application of gears were also used in small, precise devices usual focused on astronomy and the calendar.
Some gears were constructed of wood and others constructed with various types of metals. The material used depended on its use. As the centuries passed gears continued to find uses in new inventions. The first clocks incorporated very precise systems of gears. During the Industrial Revolution a multitude of machines would not be able to operate with out properly working gears.
Gears feature predominately in today’s world, especially in transportation. One modern transportation invention using gears was the bicycle, whose modern form was developed in 1885. The bicycle caused a bicycle craze in the late 19th century and many people became wealthy manufacturing bicycles. The Wright Brothers constructed their gliders and the first airplane, The Wright Flyer, from the bicycle factory they owned in Ohio. After the widespread use and adoption of the bicycle gears became used in a newer type of transportation, the automobile. The automobile uses a system of gearboxes in the transmission system to transmit power from the engine to the wheels. Today gears are used in nearly all transportation systems including railroads and airplanes, as well as other common appliances and industries such as pumps, power plants, energy systems, lifts, and elevators.
Continue reading more about the exciting history of science!